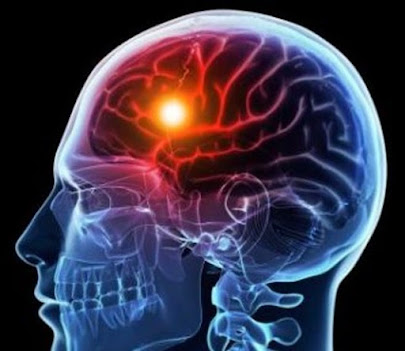
Strokes are brain attacks. They occur when the blood supply to the brain becomes blocked. A stroke is a medical emergency that needs immediate medical attention. Stroke can be defined as abrupt onset of a focal neurological deficit lasting more than 24 hours. It is also called cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or apoplexy. An acute stroke refers to the first 24-hour-period of a stroke.
The majority of strokes occur when blood vessels to the brain become narrowed or clogged with fatty deposits called plaque. This cuts off blood flow to brain cells.
Stroke is classified on the basis of its aetiology as either ischaemic (87%)or haemorrhagic (13%).
*Ischaemic stroke is produced by occlusion of a cerebral artery [thrombotic or atherosclerotic (50%), embolic (25%) and microartery occlusion, “lacunar stroke”, (25%)].
*Haemorrhagic stroke is caused mainly by spontaneous rupture of blood vessels or aneurysms or secondary to trauma.
Stroke remains the second leading cause of death at the global level and in the European region. Of the 56 million deaths that occur every year worldwide, 10.8% are due to stroke. Eighty-five per cent of these stroke deaths among all ages occur in developing countries.
The word “stroke” was likely first introduced into medicine in 1689 by William Cole in A Physico-Medical Essay Concerning the Late Frequencies of Apoplexies. Before Cole, the common term used to describe very acute nontraumatic brain injuries was “apoplexy.” Apoplexy was used by Hippocrates circa 400 BC.
Situational Depression: Understanding a Common Emotional Response
-
Situational depression is a temporary emotional response to a specific life
event that causes significant stress or disruption. It often arises after
exp...